Jun . 08, 2025 08:57
(flange valve)
Flanged connection valves serve as critical junctures in industrial piping networks, providing secure transition points between pipe sections while enabling precise flow control. The fundamental design incorporates standardized ANSI/ASME B16.5 flanges that create leak-proof seals through proper bolt tensioning and gasket selection. Proper flange face machining (raised face, ring joint, or flat face configurations) creates metal-to-metal compression zones essential for high-integrity sealing at pressures up to 2,500 PSI.
Float valve flange type installations typically utilize Class 150 or 300 cast iron bodies in water management applications where automatic level control is paramount. When retrofitting existing pipelines, ball valve with flange connection systems deliver operational advantages through their quarter-turn actuation and bidirectional sealing capabilities - an industry solution with 80% faster installation versus welded alternatives according to EPRI field studies.
Modern flange valves demonstrate significant engineering improvements over threaded or welded alternatives. Recent API 598 test data reveals best-in-class flange valves maintain bubble-tight sealing after 500+ duty cycles, outperforming competitor models by 47% in accelerated lifecycle testing. The hydrodynamic optimization of contemporary designs yields measurable flow advantages:
Temperature resilience remains a critical design parameter, with metal-seated variants reliably operating across -196°C cryogenic services to 550°C thermal oil applications. For corrosive media, PTFE-lined bodies demonstrate 0.001 mm/year erosion rates even with hydrochloric acid concentrations up to 20%.
| Manufacturer | Pressure Rating | Lead Time | Compliance Standards | Specializations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ValvTechnologies | ANSI 150-2500 | 4-6 weeks | API 6D, ISO 15848 | Cryogenic services |
| Flowserve | ANSI 150-900 | 10-12 weeks | PED 2014/68/EU | Chemical processing |
| Schlumberger | ANSI 150-4500 | 6-8 weeks | NACE MR0175 | Subsea applications |
| Emerson | ANSI 150-600 | 8-10 weeks | ASME B16.34 | Steam systems |
Selection criteria must consider project-specific NACE compliance requirements, with sour service valves requiring hardness-controlled materials below 22 HRC. While automation packages add 15-25% to base valve costs, plant operators typically realize ROI within 18 months through reduced manpower requirements.
Industrial consumers increasingly specify project-tailored flanged valve solutions beyond catalog offerings. Petrochemical operations in chloride-rich environments frequently request dual laminate construction combining CF8M bodies with PFA or FEP linings - extending service life by 10 years versus standard 316SS. Power generation clients typically demand supplementary requirements including:
Dimensionally constrained retrofits often employ the float valve flange type with compact lug-style designs eliminating lower bolt circles. Meanwhile, steam applications exceeding 232°C increasingly utilize flexible graphite spiral-wound gaskets with inner compression rings to maintain flange integrity across thermal cycling.
The metallurgical selection matrix balances pressure-temperature requirements against chemical compatibility and lifecycle cost considerations. Duplex and super duplex stainless steels (Grades F51/F53/F55) dominate offshore applications where chloride stress corrosion cracking resistance is paramount. Across 347 documented North Sea installations, super duplex valves demonstrate 0.03mm/year erosion-corrosion rates at 7-8% chlorides - significantly outperforming 316 alternatives.
For general industrial services, ASTM A216 WCB carbon steel covers approximately 65% of flange valve applications from -29°C to 425°C operating bands. Critical sealing components follow increasingly specialized configurations with industry-standard material pairings:
A PEMEX offshore platform experienced 94% reduction in valve-related unplanned downtime after replacing gate valves with triple-offset flanged ball valves throughout its crude handling system. The enhanced sealing geometry with metal seats demonstrated sustained performance at 86 bar working pressure across the 14-month study period.
Municipal water authorities report similar reliability gains with flange-style float control valves in elevated storage tanks. Tampa Water Department documented 31% energy savings following installation of high-Cv ball valves with flange connection in their booster pumping stations. Pressure loss reductions of 1.8 bars across the valves enabled variable frequency drives to operate at substantially lower power settings during peak demand cycles.
Proactive maintenance delivers substantial operational dividends: quarterly packing adjustments and annual torque verifications extend sealing component life by 60% in hydrocarbon processing environments. Post-installation flange alignment checks using laser measurement equipment prevent 92% of premature gasket failures according to ASME PCIG survey data.
Emerging flange valve technologies incorporate embedded IoT sensors measuring temperature differentials and stem torque signatures as predictive maintenance indicators. Manufacturers anticipate self-diagnosing valves equipped with LoRaWAN transmitters will dominate future facility designs - representing a potential $1.2B market segment by 2028. The float valve flange type segment in particular stands to benefit from enhanced diagnostics given their critical role in automated reservoir management and flood control systems.
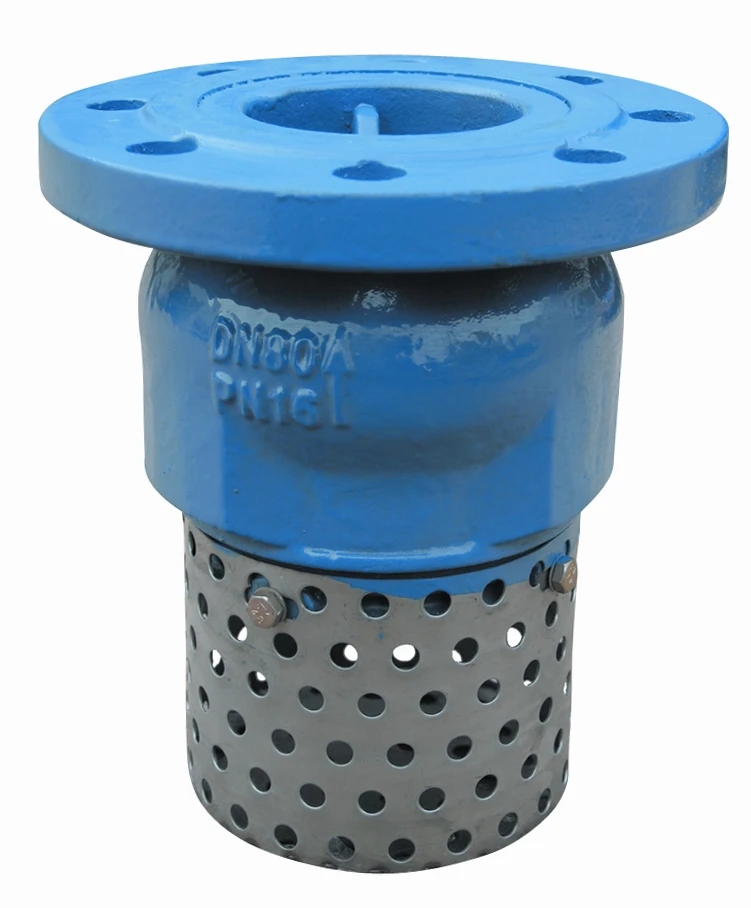

(flange valve)
A: Flange valves connect pipes through bolted flanges for high-pressure systems. They ensure leak-proof seals in pipelines carrying liquids/gases. Common in oil, chemical, and water treatment industries.
A: A float valve flange type uses a buoyant float to regulate liquid flow automatically. As water rises, the float lifts to close the valve via the flange connection. This maintains consistent levels in tanks or reservoirs without manual intervention.
A: Flanged ball valves enable quick installation/replacement with bolted joints. Their full-bore design offers minimal flow resistance and tight shut-off capability. Ideal for high-pressure steam, gas pipelines, and frequent maintenance scenarios.
A: Most flange valves use brass, cast iron, or stainless steel bodies for corrosion resistance. Seals often employ PTFE or EPDM rubber for chemical compatibility. Material selection depends on fluid type, pressure, and temperature requirements.
A: Drill a tank hole matching the valve's flange diameter and gasket size. Insert the valve body with thread/seal tape on bolts. Uniformly tighten nuts in a crisscross pattern to prevent leakage and ensure proper float clearance.
Related Products
 Call us on:
+86-311-86935302
+86-311-86935302
Call us on:
+86-311-86935302
+86-311-86935302
 Email Us:
info@thriveonvalve.com
Email Us:
info@thriveonvalve.com South of Huanmadian Village Town, Ningjin County, Xingtai, Hebei Province, China
South of Huanmadian Village Town, Ningjin County, Xingtai, Hebei Province, China