Jan . 13, 2025 09:35
Selecting the correct type of valve for an industrial application requires an understanding of the distinctive mechanisms and specific uses each valve type offers. Valves serve as the pivotal control devices in fluid handling systems, ensuring safety, reliability, and efficiency.

Let's delve into the most commonly used valve types, illustrating their unique characteristics, advantages, and suitable applications to guide you in making informed decisions for your operation.
Ball Valves Known for their durability and reliability, ball valves employ a spherical disc to control the flow. They provide a firm seal and are ideal for applications requiring tight sealing, such as gas flow systems. Their simple design offers long operational life and is capable of handling high pressure and temperature, but they are not suitable for throttling purposes due to flow regulation being binary.
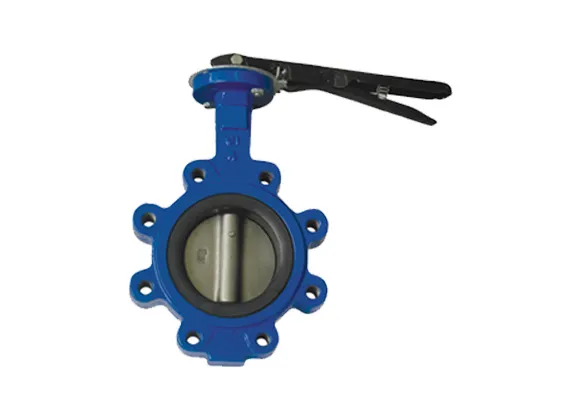
Butterfly Valves These valves are excellent for large-diameter pipelines due to their lightweight and compact design. Featuring a disc mounted on a rotating shaft, butterfly valves can throttle or isolate flow efficiently. The diverse range of elastomeric and metal seats enhances their functionality across a wide spectrum of pressure and temperature scenarios, making them invaluable in chemical, water treatment, and HVAC systems.
Gate Valves Gate valves utilize a gate or wedge barrier that moves perpendicular to the flow direction to start or stop the fluid. While excellent for on/off control, they are not suited for flow regulation due to their inability to regulate precise flow and risk of erosion. Gate valves thrive in applications requiring infrequent operation, low-pressure loss, and a bi-directional customarily deliverable in municipal water, oil, and gas applications.
Globe Valves When it comes to throttling, globe valves are unmatched. Their linear motion disc in parallel alignment to the flow allows for precise modulation. The streamlined design ensures minimal leakage in isolation, making them optimal for complex fluid control applications in steam and cooling systems. However, the flow control properties come at the cost of pressure drops across the valve.
valve types and uses
Check Valves Check valves serve the essential purpose of preventing backflow, safeguarding equipment and piping from potential damage.
These valves automatically activate with the flow, making them indispensable in pumping systems. Available in swing, lift, and diaphragm models, check valves offer flexible options to cater to diverse needs, though special attention should be given to closing pressures to avoid system instability.
Diaphragm Valves These versatile valves feature a flexible diaphragm that seals the flow. Ideally suited for corrosive or abrasive applications, they provide optimal performance in chemical processing environments. Operating with linear motion to pinch the diaphragm, they ensure there are no leaks or contamination, though they are restricted by pressure ratings and temperature limitations.
Needle Valves Precision is paramount in needle valves, where fine control over fluid flow rates is required. By employing a small plunger that fits into a seat, these valves are vital in calibration, dosing, and bleed-off applications, especially within a laboratory or process-rich environment. Despite their precision advantages, they are not intended for high-flow bulk applications due to size constraints.
Plug Valves Simplistic design and versatile operations are hallmarks of plug valves. Utilizing a cylindrical or tapered plug to open or block flow, they are proficient in handling slurry and vacuum services with minimal pressure drop. Plug valves are available in multiport designs, improving operational efficiency and reducing the need for excess valve infrastructure.
For operators and engineers, understanding these valve types offers the expertise needed to optimize systems effectively. Each valve’s authority in specific uses makes it essential to not only understand the operational environment but to anticipate demands such as pressure, flow rate, and temperature. Trustworthiness in valve selection assures safety, stability, and longevity in industrial applications, thereby fortifying system integrity and performance.


 Call us on:
+86-311-86935302
+86-311-86935302
Call us on:
+86-311-86935302
+86-311-86935302
 Email Us:
info@thriveonvalve.com
Email Us:
info@thriveonvalve.com South of Huanmadian Village Town, Ningjin County, Xingtai, Hebei Province, China
South of Huanmadian Village Town, Ningjin County, Xingtai, Hebei Province, China